![]()
Solar array
The solar array on
the SPOT 5 satellite is identical to that on SPOT 4. It is composed of five
panels covered with photocells.
The solar panels are made of a rigid honeycomb structure and a carbon-fibre
skin. The boom connecting the panels to the satellite structure is made of
carbon tubing. The deployed array has a total surface area of 25 square metres.
The solar panels have 8,640 silicon photocells (size: 24 cm²) bonded on each
face, generating a total power of over 2,400 watts.
The solar array drive mechanism orients the panels so that they track the
Sun.
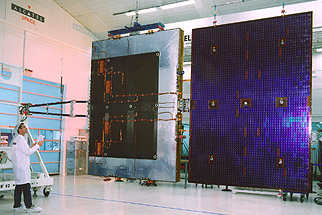
SPOT solar array
Batteries
SPOT 5's orbit means that its solar array is in
Earth's shadow for about 35 minutes and illuminated for 65 minutes during
each orbital revolution. The solar cells only generate current when illuminated,
so it must be stored during the day to maintain power to the satellite during
eclipse periods.
Likewise, the satellite needs to be powered during launch phases before the
solar array is deployed.
To store power, SPOT 5 has four 40 ampere-hour batteries identical to those
on SPOT 4. Each battery is composed of 24 nickel cadmium cells.
The batteries are charged on the ground before launch to provide the satellite
with sufficient power for three orbits until the solar array is deployed.
To meet the five-year end-of-life power requirement (over 25,000 cycles), battery charge has to be finely controlled.
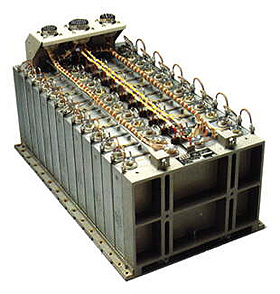
SPOT battery
Electrical power control and
regulation
Battery charge is managed nominally by the flight software, which controls the junction shunt regulator. As its name suggests, this regulator diverts excess current using a shunt arrangement.

Junction shunt regulator and distribution (RSJD)
Nominal charge control cycle:
- at night, all satellite power is supplied by the batteries, which discharge, and the bus voltage decreases;
- as soon as the solar array is illuminated, the charging phase begins; the battery charging current is kept constant at 48 amperes and the voltage increases;
- when the voltage reaches its threshold, the shunt regulator maintains it at this value;
- once the battery recharge coefficient is reached, the onboard processor sends a command to stop charging and maintains the current at 0.4 amperes.
In safe mode, the onboard processor is inoperable and battery charge and solar array power are controlled autonomously by hard-wired logic circuits.
Electrical power distribution
Power is distributed to the satellite subsystems. The main power bus feeds branch buses that power the spacecraft bus, payload, passengers, and the bus and payload heating systems. A regulated 50-volt bus powers the central processor and other critical systems. The shunt regulator controls power distribution.