![]()
The DORIS system (Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite) was designed and developed by CNES, GRGS, the French space geodesy research centre (attached to CNES, the French national scientific research centre CNRS, and Paul Sabatier University) and IGN, the French survey and mapping agency. Its objective is to meet new requirements for precise satellite orbit determination and ground beacon location.
 |
 |
 |
The spaceborne DORIS instrument uses Doppler techniques to measure the velocity of a satellite relative to a permanent network of 60 orbitography beacons operating in more than 30 countries:
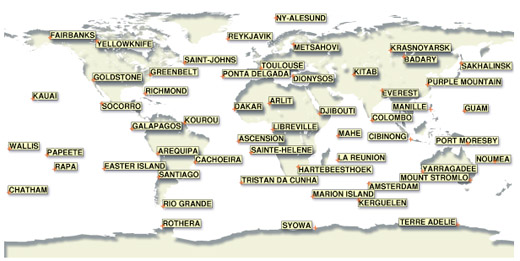
Permanent network of DORIS orbitography beacons
Measurements acquired by the beacon network are processed and gravitational and other forces acting on the satellite are modelled to determine its precise trajectory. A satellite's altitude can thus be calculated with an accuracy of 10 to 20 centimetres within 24 hours. Refined processing improves accuracy to a few centimetres within four weeks.
DORIS first flew on the SPOT 2 satellite and has since flown on SPOT 3 and SPOT 4, Topex/Poseidon, Jason-1, and most recently Envisat.It is now also a passenger on SPOT5.
SPOT 4 also features a new system called the DIODE navigator, able to determine
the satellite's orbit in real time with an accuracy of a few metres on all
three axes.
An upgraded version of the DIODE software soon to be uploaded to SPOT 4 will
make it possible to achieve sub-metre accuracy. Data are sent in real time
along with the auxiliary data in the payload telemetry.
The spaceborne component of DORIS comprises a receiver
(MVR) for measuring radial velocity, an ultrastable oscillator (OSU) and an
omnidirectional antenna. The MVR measures the Doppler shift in the frequency
of the 400-MHz and 2-GHz signals emitted by orbitography beacons.
The 400-MHz signal measurement is vital for reducing ionospheric propagation
errors.
The European Space Agency's Envisat satellite is carrying a second-generation receiver capable of receiving two orbitography beacons simultaneously. This receiver will significantly improve orbit determination accuracy.
The miniaturized second-generation receivers on Jason-1 and SPOT 5 provide the same functionality, with two channels and the DIODE navigator software.

DORIS onboard antenna

DORIS family
From left: First-generation MVR on SPOT
1, SPOT 2, SPOT 3, SPOT 4 and Topex/Poseidon
Second-generation MVR on Envisat
Miniaturized second-generation MVR on Jason-1 and SPOT 5
DORIS instruments also locate ground location beacons (GLBs). The system is thus used chiefly by the scientific community to monitor and track:
- tectonic plate motions of the order of a few centimetres a year
- vertical ground displacements caused by deformations of the Earth's crust
- the Earth's geocentre motion
- shifts in the Earth's rotation axis
![]() More
about the DORIS system and its missions: http://ids.cls.fr
More
about the DORIS system and its missions: http://ids.cls.fr